Tie Lines and the Lever Rule
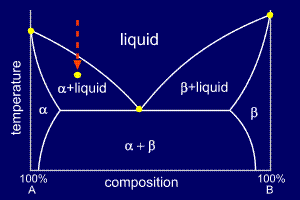
Consider a cooling alloy at the composition and temperature marked on the diagram. As shown on the phase diagram, the alloy is, at the given temperature, a mixture of alpha and liquid phases - but what are their exact compositions at this temperature?
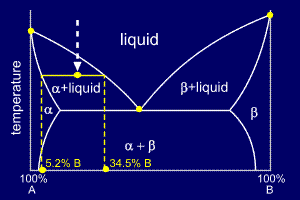
An
isothermal (constant temperature) line through the alloy's position on
the phase diagram when it is in a two phase field, intersecting the two
adjacent solubility curves, is called a tie line (yes, that's the
horizontal yellow line on the diagram).
The
ends of the tie lines show the compositions of the two phases that
exist in equilibrium with each other at this temperature. From the
diagram we know that alpha and liquid phases will exist. The tie line
shows that the alpha phase is 5.2%B and the liquid phase is 34.5%B at
this temperature.
Remember,
though, that the overall composition of the sample is unchanged - we
are only discovering the compositions of the constituent phases within
the sample.
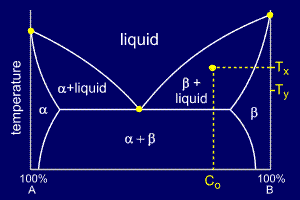
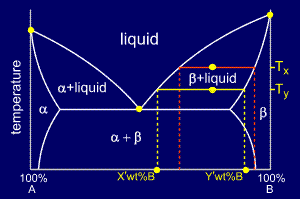
For a cooling alloy at composition Co and temperature Tx , tie lines may be used to answer questions such as:
•what phases are present ?
•what are their compositions ?
•if the temperature is reduced to Ty, how do the compositions of the two phases vary ?
The
answer to "what phases are present ?" is easy. Composition Co and
temperature Tx meet in the beta + liquid phase field, so these are the
two phases present.
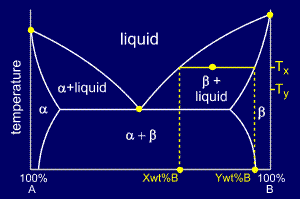
To
answer "what are their compositions ?" we must draw a horizontal tie
line from the point to the nearest phase diagram boundaries. The tie
line shows us that the compositions are:
•Liquid: X wt% B
•Beta: Y wt% B
Tie Lines and the Lever Rule
To
answer the last question "if the temperature is reduced to Ty, how do
the compositions of the two phases vary?" consider the new tie-line,
shown in yellow on the diagram.
The compositions of liquid and beta phase have both decreased in wt%B to:
•Liquid: X' wt% B
•Beta: Y' wt% B
Thus, both the liquid and the beta phases are getting richer in A as the sample is cooled.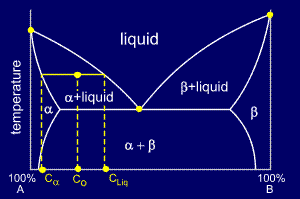
Now
that we know the compositions of the two phases, we need to find how
much of each phase exists at the given temperature. The ratio of the two
phases present can be found by using the lever rule.
At
first sight the lever rule can appear confusing. It is really invoking
the conservation of mass, and can be proved mathematically, as shown
below the diagram.
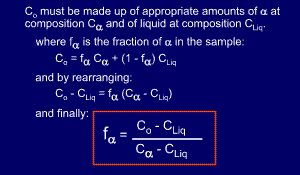
Essentially,
we start off with an overall composition of our alloy - Co. From the
tie-line we know that the two phases at a given temperature have two
different compositions, but overall the amounts of these two
compositions must add up to the alloy's overall composition, Co.
This is the basis for the lever rule. Using the lever rule itself is very simple, we'll show you with a diagram.....
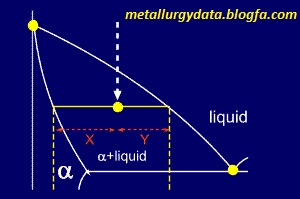
Basically,
the proportions of the phases present are given by the relative lengths
of the tie line. So, the proportions of alpha and liquid present on the
diagram (showing a portion of the whole phase diagram) are:
and
Simple, isn't it ?
But... which equation corresponds to which phase ?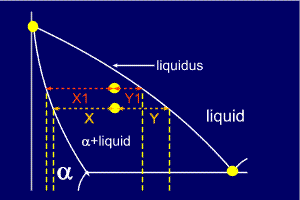
Now,
consider the same alloy as it crosses the liquidus line. It seems
reasonable to assume that, at this point, the alloy will be nearly all
liquid. Looking at the diagram it can be seen that Y1 is very small here
and so must be the proportion of alpha present. Similarly X1 is
relatively large and so it corresponds to the amount of liquid.
So,
the left side of the tie line gives the proportion of the liquid phase
(the phase to the right), and the right side of the tie line gives the
proportion of the alpha phase (the phase on the left).
Remember: you use the length of the line which is furthest from the phase in which you are interested.
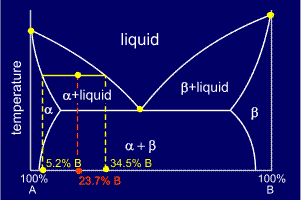
Distances
along the tie line can be found very simply by using a ruler on an
accurate phase diagram or, more correctly, by using data from the
composition axis (the x-axis).
For
example, on the diagram shown, the percentage of alpha present can be
calculated from the three pieces of composition data given:
Fraction of alpha = (34.5 - 23.7) / (34.5 - 5.2) = 0.3686
Thus, percentage of alpha = 0.3686 x 100 = 36.86%
and, as the alpha and the liquid make up 100% of the alloy's composition:
Percentage of liquid = 100 - 36.86 = 63.14%
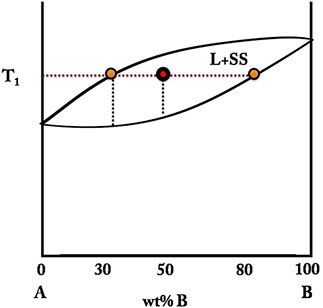
قانون
اهرم (Lever Rule) یک رابطه بسیار مهم برای هر ناحیه دو فازی در یک نمودار
دوتایی است. سیستم آلیاژی زیر را که تشکیل محلول جامد می دهند را در نظر
بگیرید.
آلیاژی
با ترکیب متوسط 50 درصد B، در دمای T1 شامل مذاب L و محلول جامد ss است.
ترکیب مذاب، 30 درصد B و ترکیب محلول جامد 80 درصد B است. در 100 گرم این
آلیاژ، 50 گرم آن باید B و 50 گرم باقی مانده آن A باشد. با فرض این که وزن
کل مخلوط 100 گرم باشد، داریم:
mss+mL=100
اگر
mss برابر با وزن فاز جامد در این آلیاژ بر حسب گرم باشد، mss-100 وزن فاز
مذاب خواهد بود. مقدار B در فاز جامد آلیاژ برابر با وزن این فاز ضربدر
درصد B در آن فاز (80%) است. به طور مشابه، وزن B در فاز مذاب برابر با وزن
فاز مذاب ضربدر درصد B در مذاب (30%) است. بنابراین:
0.3mL+0.8mss=0.5(100)=50g
با حل این دو معادله، مقادیرفاز جامد و مذاب در این آلیاژ به دست می آید:
mL=60g , mss=40g
چون
وزن کل آلیاژ 100 گرم است، درصد وزنی فاز جامد 40 و درصد وزنی فاز مذاب 60
هستند. در حالت کلی، برای هر آلیاژ با ترکیب متوسط x که در دمای ثابت شامل
مخلوطی از دو فاز α و β باشد، موازنه وزنی به صورت زیر خواهد بود:
mα+mβ=m total=%100=1 xβmβ+xαmα=x(mα+mβ)
در
این معادله، xα و xβ به ترتیب ترکیب فاز α و β، x ترکیب کلی آلیاژ، mα
درصد فاز α و mβ درصد فاز β است. با حل این دو معادله مقادیر فازها به صورت
زیر خواهد بود: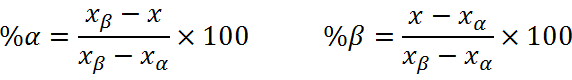
معادلات
فوق قانون اهرم را نشان می دهند. به طور خلاصه، با توجه به قانون اهرم،
برای تعیین مقادیر نسبی دو فاز در تعادل با یکدیگر در یک دمای خاص در یک
منطقه دوفازی، یک خط عمودی (ترکیب آلیاژ) و یک خط افقی دمای ثابت تا مرزهای
آن منطقه رسم می شود. خط عمودی، خط افقی را به دو بخش تقسیم می کند که طول
آن ها به طور معکوس متناسب با مقدار فاز های موجود است. نقطه تقاطع خط
عمودی با خط افقی می تواند به نقطه اتکای یک سیستم اهرم تشبیه شود.
برای
مثال برای تعیین مقادیر فازهای موجود در آلیاژی حاوی 20B-80A در دمای T،
خط عمودی که نشان دهنده آلیاژ 20B-80A است، خط رابط افقی را به دو بخش
تقسیم می کند (mn,no). اگر طول کل خط رابط (mo) صد درصد وزنی یا وزن کل دو
فاز موجود در دمای T در نظر گرفته شود، قانون اهرم را می توان به طریق
ریاضی نشان داد:![]()
اگر خط رابط از نمودار فازی برداشته شود و به جای آن مقادیر عددی جایگزین شوند: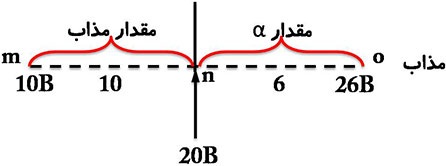
با استفاده از معادله بالا داریم: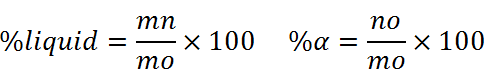
با
خلاصه کردن هر دو قانون، آلیاژی با ترکیب 20B-80A در دمای T مخلوطی از دو
فاز است. یکی فاز مذاب با ترکیب 26B-74A که 62.5% مخلوط و دیگری فاز جامد α
با ترکیب 10B-90A که 37.5% مخلوط ا تشکیل می دهد.
